nickel, Cobalt, and Beryllium Alloys
Market Insights of Inconel
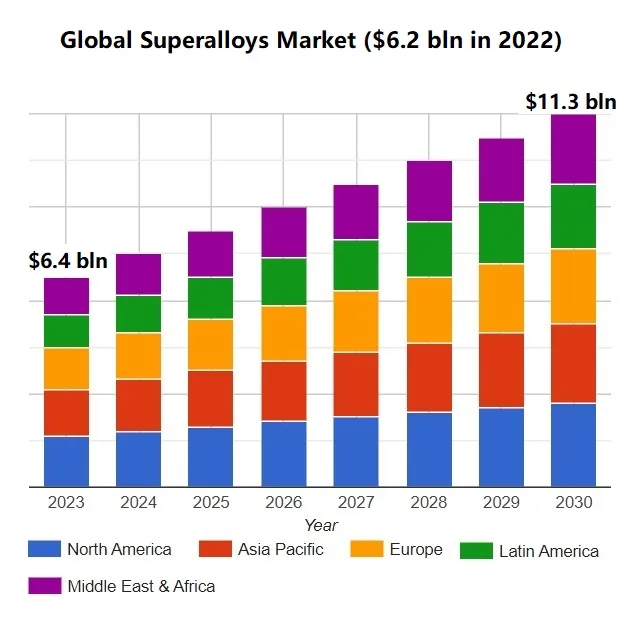
- Global Superalloys market size was valued at USD 6.4 billion in 2023 and is poised to grow from USD 6.6 billion in 2024 to usd 11.34 billion by 2030.
- The global superalloys market is witnessing significant growth due to the increasing demand for high performance materials in various industries such as aerospace, automotives, power generation and petro-chemical industries.
- Geographically, North America dominated the global superalloys market, primarily due to the presence of major aerospace and automotive manufacturers in these regions. However, emerging economies in Asia Pacific, such as China and India, are witnessing rapid industrialization and urbanization, leading to increased demand for superalloys.
- Source is from Skyquest. Click here to see detail information.
Superalloys Market Information
- NASA Glenn Research Center has developed a nickel-based superalloy using specific alloying elements to inhibit deleterious deformation at temperatures above 700°C. Click here for more information about this LEW-TOPS-152
- NASA’s new 3D-Printed superalloy can take the heat. NASA has demonstrated a breakthrough in 3D printable high-temperature materials that could lead to stronger, more durable parts for airplanes and spacecraft… Click here for more information.
- Superalloys use growing rapidly -Frost & Sullivan’s recent analysis, “Growth Opportunities for Superalloys,” finds that the industry is expanding at a rapid pace. Click here for more information.
- Researchers use new new cobalt-modified nano material to make fuel cells more robust, sustainable. Click here for more information.
What Are superalloys?
- Superalloys are group of metals that offer better creep, oxidation and corrosion resistance than traditional alloys, whilst retaining excellent mechanical properties, even at high temperatures. Hastelloy, Inconel, Monel, Stellite and Beryllium Copper are common used superalloys. Click here to see specifications of typical superalloys grades
- Commonly used in the aerospace industry for components in gas turbine engines, superalloys use a base of nickel, cobalt or copper to offer far superior properties versus traditional alloys of steel or aluminum.
- Whilst most traditional alloys based on iron start to see a significant decline in material strength at 400 degree Celsius, many superalloys actually exhibit an increase in strength between 750 and 900 degrees.
What makes superalloys unique?
- Lattice structure and precipitation hardening. At an atomic level, the elements that make up metals form lattice structures. What does this mean? The atoms are arranged in perpendicular rows and grids, unlike plastics. The natural tendency of metals to form lattice structures is both beneficial and a hindrance, affording them strength, but only in certain planes.
- Alloying a metal (along with other benefits such as oxidation resistance) helps solidify this lattice structure and increases the force required to cause atomic planes to slip, by blocking these slip planes.
- Superalloys go one step further. The formation of a two-phase equilibrium microstructure affects how the alloying elements arrange themselves and gives them protection from multiple different modes of failure, resistance to corrosion.
Why Are superalloys Important?
- Creep Resistance. Creep is a material failure mode whereby a component deforms at a stress level well below its ultimate tensile strength. Superalloys enable parts such as turbine blades to operate at the extremes of centripetal force and heat, all while retaining their strength and most importantly, their shape.
- Resistance to high temperatures.
- Resistance to corrosion.
which Industries Use superalloys?
- Aerospace
- Chemical Processing
- Oil and Gas
- Automotive
- Medical
Main Challenges to machining superalloys
- The high strength of nickel-base superalloys at cutting temperatures causes high cutting forces, generates more heat at the tool tip, and limits their speed capabilities.
- The low thermal conductivity of these alloys transfers heat produced during machining to the tool, subsequently increasing tool tip temperatures and causing excessive tool wear, which can limit cutting speeds and reduce useful tool life.
- The presence of hard, abrasive intermetallic compounds and carbides in these alloys causes severe abrasive wear on the tool tip.
- The high capacity for work hardening in nickel-base alloys causes depth-of cut notching on the tool, which can lead to burr formation on the workpiece.
- The chip produced during machining is tough and continuous, therefore requiring acceptable chip control geometry.
5 key steps to make High Quality Superalloys
Major difference between Inconel and common steel production are: 1)Inconel uses vacuum induction melting, while common steel is melted in a basic oxygen furnace or electric arc furnace, without the stringent atmosphere control; 2)Inconel requires precise temperature control and slower processing speeds during forging, while steel is easier to forge and can be formed at a wider range of temperatures.

Raw Material
- Use virgin material only, no scrap
- Virgin material enables strict control of chemical composition and greatly reduces contamination.
vacuum Induction Melting (vIM)
- Vacuum induction melting (VIM) utilizes electric currents to melt metal within a vacuum container.
- VIM offers a high level of control over the composition of the alloy.
- VIM greatly reduces the contamination (dust etc) and oxidation, while elements that are often undesired such as hydrogen or nitrogen can be removed from the process.
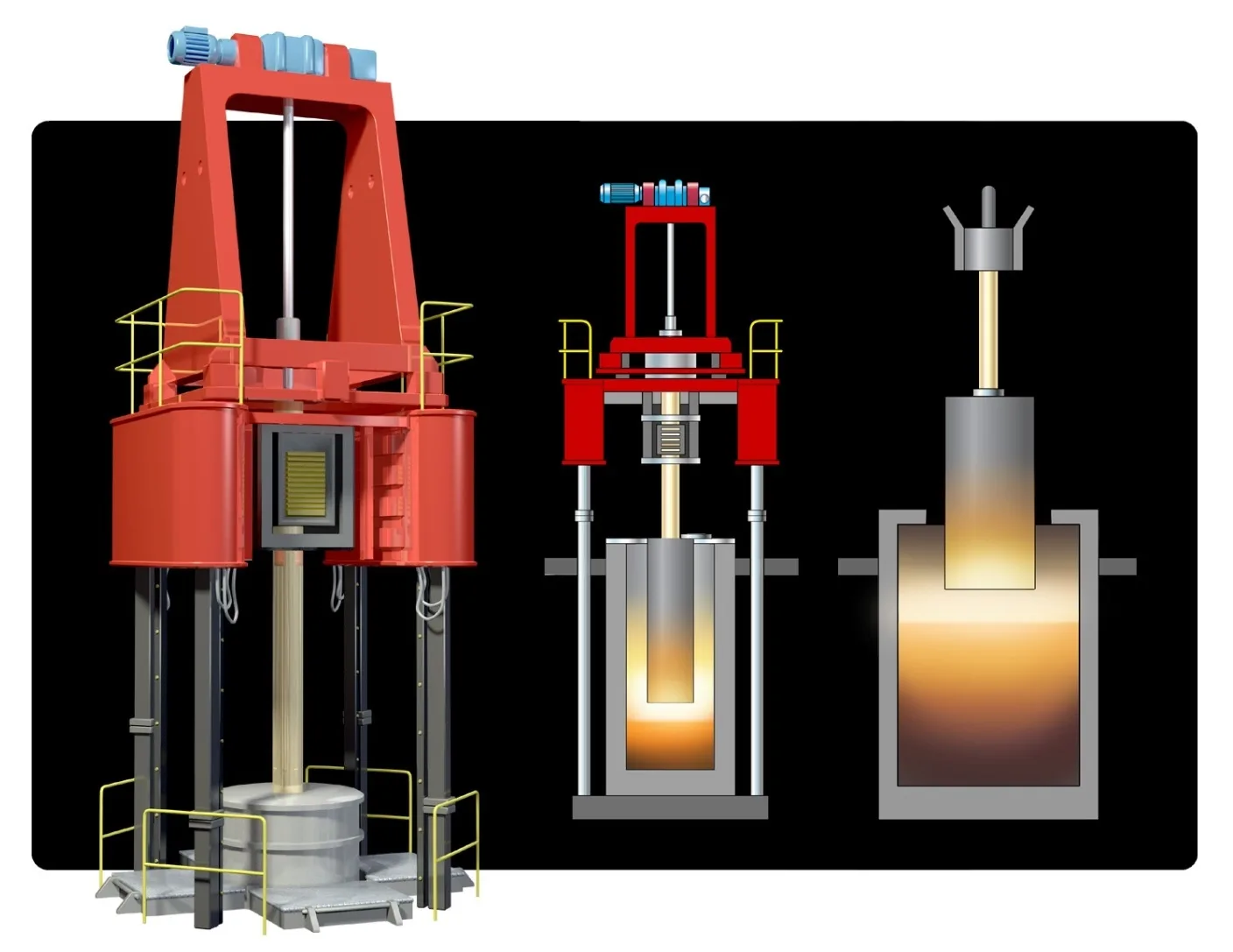
Electroslag remelting (ESR)
- Electroslag remelting (ESR), also known as electro-flux remelting, is used to remelt and refine steels and various super-alloys, resulting in high-quality ingots for for mission critical applications.
- ESR reduces inclusions, improves alloys purity.
- Alternative to ESR, another method is VAR, vacuum arc remelting.
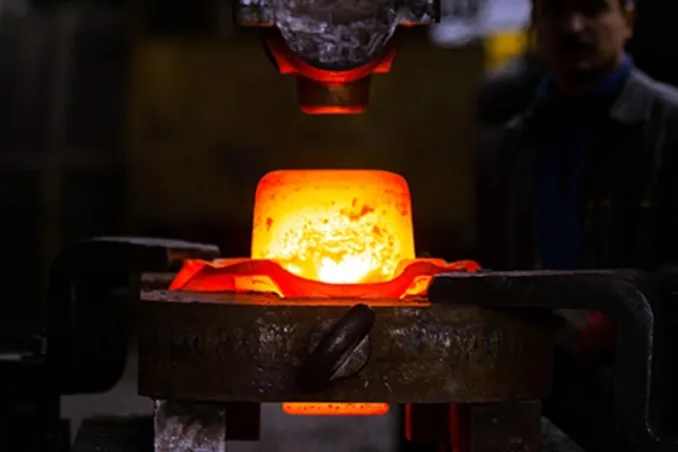

Forging
- Metal is shaped during the forging process.
- Alloy’s internal grain texture deforms to follow the general shape of the part. As a result, the texture variation is continuous throughout the part, giving rise to a piece with improved strength characteristics.
- Strictly control forging temperature is critical, since superalloy’s forging temperature range is narrow.
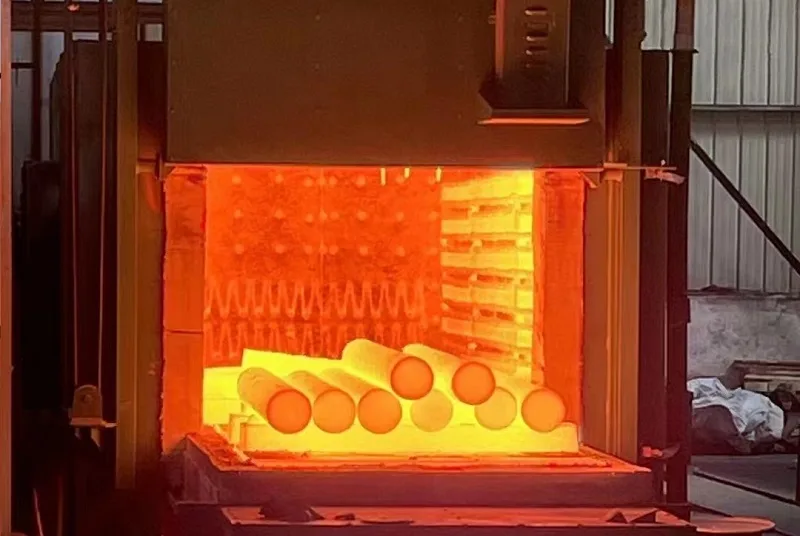

Heat Treatment
- Solution Annealing
- Age Hardening
Renowned Inconel suppliers
About Sintermatic Industrial Inc.
- Founded in 2006, Sintermatic Industrial Inc is a private manufacturer specializing in producing Superalloy materials of Inconel, Monel, Hastelloy, Stellite, Beryllium Copper, as well as machined parts. We have vertical integrated capabilities of melting, forging, heat treatment, machining and sintering process. Click here to find more details about us
- Our key advantages are: Vertical integrated capabilities from melting to final machining; Accommodate low volume order; Short Lead Time. Click here to see detail information.
Email us
ming@stmtus.com
Call Us
1 (840) 240 9993
Address
17890 Castleton Ste. 398 Rowland Height, CA91748 US
